

One of the most essential components of SEO is keywords.
We'll teach you how to use keywords for SEO in this article so you can increase your search visibility.
Keywords are search terms that people enter Google (or another search engine), and they provide you the chance to show up in search results when your website contains pertinent content.

Depending on the main topic of the text, we frequently discuss keywords in three categories:
• Primary keywords: The term that a webpage aims to rank for in searches. It is the page's primary subject. The main keyword "how to make a smoothie bowl" could be the focus of an article about creating one.
• Secondary keywords: Synonyms or longer, more focused variations of the main keyword, sometimes known as long-tail variants. Because searchers are typically looking for similar solutions, secondary keyword search results are typically extremely similar to primary keyword search results.
Search engines look for certain terms in your content to determine whether it is relevant to a given query, so knowing how to use keywords for SEO is crucial.
This is crucial to getting people to visit your website.
Seldom do users browse past the first page of search results. since the first few results usually contain what they're looking for.
You must conduct keyword research to choose which terms to put on your website. It's a procedure that entails determining the search terms used by your intended audience.
Although it is possible to accomplish this manually, using a keyword research tool is the most effective way to identify useful and relevant search phrases. These programs offer you stats to assist you in identifying the most promising possibilities in addition to keyword ideas.
The primary guideline for using keywords is to include them organically.
To help visitors and search engine crawlers comprehend the subject matter of your material, you should include keywords in certain areas.
1. H1 Tags and the title
The title tag (HTML that indicates the page title for search engines and browsers) and the H1 tag (HTML that provides the title on the actual webpage) are scanned by search engine bots when they crawl your webpage in order to determine the topic of the content.
The H1 and title tag ought to resemble one other.
Why?
because search results frequently display title tags. Therefore, if a user clicks on a result and is taken to a webpage with a different title, they will be perplexed.
2. Header and Subheader sections
Your material can be more easily navigated by users and search engine crawlers if it is divided into sections using headings and subheadings (H2-H6).
Because of this, subheadings are excellent locations to include any auxiliary keywords you wish to rank for.
3. Principal Content of the Body
The main body content of your page should have organically occurring references to your primary, secondary, and semantic keywords. This lets visitors and search engine crawlers know that your page is pertinent to a particular query.
As a general guideline, the first paragraph should contain the main keyword. in order for visitors to grasp the page's purpose with ease.
There is a fallacy here: keyword density has no bearing on rankings. Keep your keyword usage natural instead.
4. Using Anchor Text
The clickable copy in anchor text links to an email client, another website, or another page.
Using the keywords from the connected pages as anchor text is a smart approach when creating links to other pages on your website.

Why should I connect to pages on your website?
Considering that doing so aids users in finding relevant content that they would find interesting. Additionally, it facilitates search engines' ability to locate pages on your website.
In particular, attempt to keep anchor text to no more than five words. Additionally, take care not to always utilize the same anchor text. Mix primary and secondary keywords instead.
5. Alt tags for images
Screen readers can read aloud alternative text, or alt text, which is an HTML element that describes a particular image on a page and appears on the page in the event that the image cannot load.
Alt text helps search engine crawlers understand the purpose of an image. This implies that using alt tags with your main or secondary keywords will help you show up in image-based search results, bringing even more people to your website.
Alt tags have uses beyond SEO; they are crucial for accessibility. Screen readers are used by visually impaired people who depend on them to interpret what visuals on a webpage represent.
When searching for the target keyword on Google Images, the identical image comes up as well.
Remember that decorative images, such graphic illustrations that don't provide any information, don't require alt text.
Regarding the duration, there isn't a set recommendation. However, because screen readers have character limits, it's advisable to maintain it at 125.
6. URL Shorthand
The final portion of a URL that serves as a page identification is called a URL slug. Additionally, this is a great location for a page's main keyword to appear.
Plus, from the perspective of user experience, it makes sense to use your goal keyword in the URL slug. A user can increase the likelihood that someone else will click on the link if they forward it to them since they would instantly understand the purpose of the page.
When feasible, try to keep the slug under five words while yet including as much information as possible about the subject.
7. Description Metaphor
An HTML element known as a meta description gives a succinct (one or two sentences) explanation of the content of the webpage.
It's still an excellent spot to use your main keyword to draw people to your website even when it's not a ranking factor.
Additionally, it is sense to provide the most crucial details first in your meta description. to ensure that it is readable and does not get truncated in the event that your meta description is shortened.
Common Keyword Usage Errors to Prevent
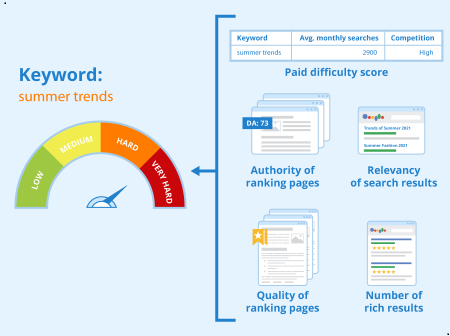
After learning how to employ keywords for SEO, it's time to discuss common pitfalls to avoid in order to increase your chances of ranking highly.
8. Stuffing Keywords
In an attempt to manipulate search results, keyword stuffing is a negative SEO practice that involves artificially pushing as many terms as possible onto a webpage.
Even if a webpage mentions a specific keyword, modern search algorithms are sophisticated enough to recognize when it is not relevant to the query entered.
There isn't a strict guideline for how many keywords you should use for SEO. As we've already covered, keyword density has little bearing on rankings.
However, cramming your page with keywords will almost definitely lower your rankings.
9. Disregarding the Search Intent
It's critical to satisfy search intent because search engines aim to deliver relevant results.
They achieve this by analyzing the user's purpose and delivering results that align with it.
The four categories of search purpose that keywords are usually categorized into are transactional, commercial, navigational, and informative. Poor search performance also results from disregarding the search intent of a keyword.
Even if your page is otherwise highly optimized for your main term, this still holds true.
It is unlikely that the article will rank for the target term, regardless of its quality. because its purpose is informational rather than commercial.
10. Absence of a Keyword Plan
A strategy for keywords is a plan that specifies which keywords you want to rank for, what kind of content you will use to target them, and how important each keyword is.
Using a strategy, you can identify and focus on keywords that will help you reach a particular objective and have the most commercial potential. like raising conversion rates.
Also Read :
Keyword Strategy in SEO: How to Create New Keyword
How to Understand Your Organic CTR and Make It Better
How To Perform a Quick SEO Audit of a Website