

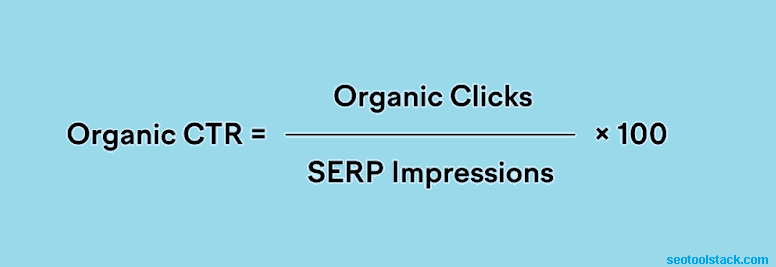
When we say "organic," we're talking about the number of clicks to views on organic search results. CTR stands for "Click-Through Rate." To put it more simply, it's a way to see how many people click on your search result when they see it in a list, even if you haven't paid to promote it. It's a useful way to figure out how well your website or material is naturally getting people to click on it.

For example, if there are 1000 searches for “keyword.” A link to your site shows up every time in the results. Your page receives 150 clicks.
Your organic CTR would be 15% (15 out of 100).
More traffic from Google and other search engines will come to your site if your direct click-through rate is high.
No,
Google doesn't use organic CTR as a direct ranking factor to decide where your page shows up in search results. But the relationship is more complicated than that. Google doesn't use CTR as a ranking factor, but it can affect your results in other ways.
How it works: Should your page show up in search results and more people click on it than other sites, Google may think that your page is more important or relevant. If more people click on your page over time, it might move up in the results.
Even though CTR isn't a direct factor, it's still important because it shows how engaged users are with your content and how valuable they think it is. If your CTR is high, you might get more attention and, eventually, better results.
Of course! You can use these steps to find out the CTR for a certain search query:
1. Search Console from Google:
Sign in to your Google Search Console account.
Pick out your website's address.
In the menu on the left, find "Performance."
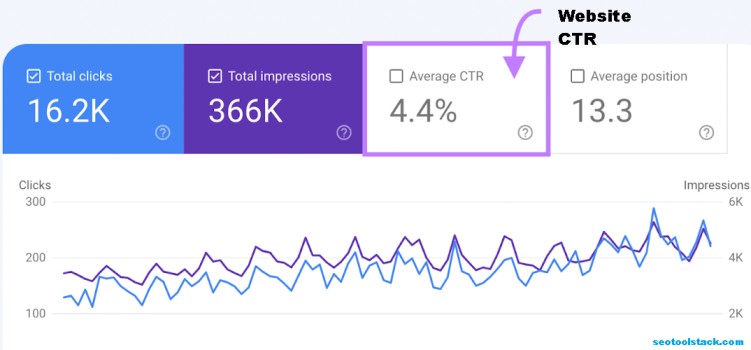
A graph will show you the number of clicks, impressions, click-through rate, and average location.
You can see a list of search terms by clicking on the "terms" tab.
You can see the CTR for the exact question you want to look into.
2. Analytics Tools:
If you use Google Analytics or another analytics tool, you might find similar data in the "Acquisition" or "Search Console" groups.
You can drill down to see how certain questions are doing and what their CTR is.
2. Manual Calculation:
To figure out CTR by hand, use this formula: CTR = (Clicks / Impressions) * 100.
For instance, if 1,000 people saw your page and 100 clicked on it for a certain question, the CTR would be (100 / 1,000) * 100, which equals 10%.
Tracking CTR for specific queries lets you know how well your content fits what users are looking for with those queries so you can make changes to your pages to make them work better.
The best organic click-through rate (CTR) can change depending on the business, the type of material, and the search query. Most of the time, you want a bigger CTR because it means that more people who see your page in the search results are clicking on it. But different people may have different ideas about what a "good" CTR is.
To give you an idea, here are some broad guidelines:
Low CTR: If your CTR is less than 1%, it could mean that your result isn't very interesting or useful for the query.
Average CTR: A normal CTR is between 1% and 5%.
High CTR: A CTR of more than 5% is usually a good thing, especially for queries that are very narrow or targeted.
To raise your organic click-through rate (CTR), you need to make your search listings more useful and appealing by optimizing different parts of them. There are a number of things you can do:
1. Compelling Titles:
Make names for your pages that are catchy and clear, and explain what the page is about.
Display relevant keywords to show the searcher that your material fits the criteria.
2. Meta Descriptions:
Make meta descriptions that are interesting and give a brief summary of your material.
Use wording that gets people to take action and stress how important it is to click on your result.
3. Rich Snippets:
Use organized data and rich snippets to improve your search results.
This can include reviews, star ratings, product details, and other things that will make your result stand out.
4. Improve the structure of URLs:
Make sure your URLs are clean, short, and have important keywords.
A URL that is easy to read can make your result more trustworthy and encourage people to click on it.
5. Make use of Schema Markup:
Add schema code to your content to give search engines more information about it.
This could make rich bits better and help them show up higher in search results.
6. Content of High Quality:
Make material that is useful, informative, and of high quality that directly answers user questions.
People are more likely to click on content that fixes problems or gives them new ideas.
7. Page Load Speed:
Improve the speed at which your website loads to give users a good experience.
People are more likely to click on results that load fast.
8. Mobile Optimization:
Many people search for things on their phones these days, so make sure your website works well on those, too.
Google also gives mobile-friendly sites more weight in its results.
9. A/B Testing:
Try out different content, meta descriptions, and even titles to see what works best for your readers.
You can improve your method by using A/B testing to see how real users react to it.
10. Use Actionable Language:
Use words that people can act on in your titles and meta descriptions.
Use words like "Learn more," "Discover," or "Get started" to get people to do something.
11. Understand User Intent:
Make sure that your content fits the user's search question.
Think about what people will want and give it to them clearly and concisely.
12. Watch out for analytics:
Check your website's data often to see how CTR is changing.
Find the pages that are working well and the ones that aren't to improve your approach.
Keep in mind that increasing CTR is an ongoing process, and it's important to change your tactics as users' habits and search engine algorithms change.
Also Read:
What Is Silo SEO and Is There a Better Option?
A Qualified SEO Expert Must Have Six Key Skills
The 11 Deadly Sins of Search Engine Optimization